Bridges
What are Dental Bridges?
Purpose:
To replace missing teeth and restore the functionality and aesthetics of your smile.
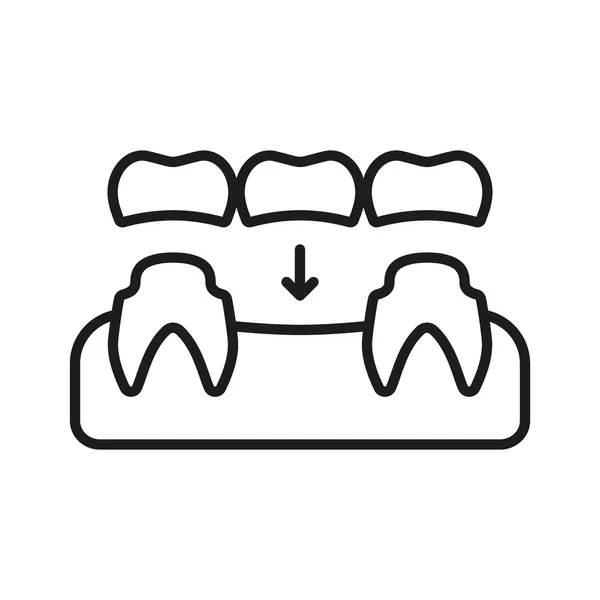
A dental bridge is a fixed (non-removable) prosthetic device used to replace one or more missing teeth by anchoring to adjacent natural teeth. It consists of a false tooth (or teeth) called a pontic, which is held in place by abutment teeth. Bridges can be made of various materials like porcelain, ceramic, or gold and are a common solution for restoring both the appearance and function of your smile.
Components:
Pontic: The false tooth or teeth that fill the gap.
Abutment teeth: The natural teeth or implants on either side of the gap that support the bridge.
Types:
Traditional Bridges: Rely on crowns cemented onto the abutment teeth.
Cantilever bridges: Supported by a crown on only one side of the missing tooth.
Materials:
Bridges can be made from a variety of materials, including:
Porcelain Fused to Metal (PFM): A type of dental restoration that combines the strength of a metal base with the aesthetic appeal of porcelain. The porcelain layer mimics the appearance of natural teeth
Porcelain: No metal underneath. Offers a more natural look and can be matched to your existing tooth color.
Why Choose a Dental Bridge?
*
Why Choose a Dental Bridge? *
Restores chewing and speaking ability: Bridges help you eat and speak comfortably.
Maintains facial structure: Helps prevent teeth from shifting and altering your facial appearance.
Improves aesthetics: Bridges can restore a natural-looking smile.
More affordable than implants in some cases: Bridges can be a less expensive option than dental implants.
Faster treatment: Bridges can often be placed in fewer appointments than implants.
How are Dental Bridges Fitted?
1. Tooth Preparation: The dentist prepares the abutment teeth by removing some enamel to create space for the crowns.
2. Impression: An impression of your teeth is taken to create a model for the dental lab.
3. Temporary Bridge: A temporary bridge may be placed to protect your teeth and gums while the permanent bridge is being made.
4. Permanent Bridge Placement: The permanent bridge is fitted, adjusted, and cemented or bonded in place.
Important Considerations:
Maintenance:
Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups are crucial to maintaining the health of your bridge and the surrounding teeth.
Lifespan:
Dental bridges can last for 5 to 15 years or longer, depending on factors like material, oral hygiene, and the health of the supporting teeth.
Alternatives:
Consider dental implants as an alternative, especially if you have healthy jawbone and prefer a more permanent solution.