Fillings
Dental fillings are a common treatment to repair teeth damaged by decay or injury. The process involves removing the damaged portion of the tooth and then filling the cavity with a durable material. This restores the tooth's shape, function, and strength, preventing further decay from spreading.
Types of Dental Fillings:
Direct Fillings:
These are placed directly into the prepared tooth cavity in a single visit. Common materials include:
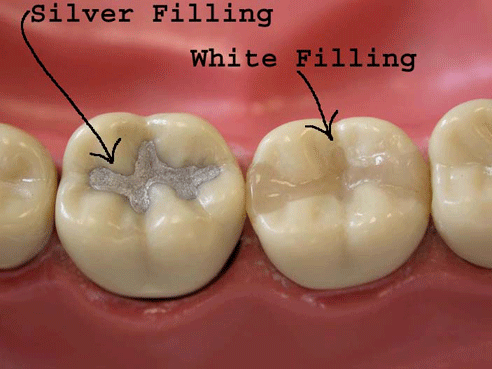
Amalgam: Silver-colored, made of mercury, silver, tin, zinc, and copper.
Resin Composite: Tooth-colored, made of a resin base with powdered quartz, silica, or glass.
Indirect Fillings:
These are custom-made in a dental lab based on an impression of the prepared tooth and require a second visit for placement. Examples include inlays, onlays.
Procedure for Dental Fillings:
Numbing: The area around the affected tooth is numbed with a local anesthetic.
Decay Removal: The decayed or damaged portion of the tooth is removed using a drill, air abrasion instrument, or laser.
Cleaning: The cavity is cleaned to remove any remaining decay or debris.
Filling Placement: The chosen filling material is placed into the cavity.
Shaping and Polishing: The filling is shaped and polished to ensure a comfortable bite.
When are Fillings Used?
Cavities:
Dental fillings are the primary treatment for cavities, which are holes in the teeth caused by tooth decay.
Minor Chips and Cracks:
Fillings can also repair minor chips and cracks in the teeth, restoring their appearance and preventing further damage.
Replacement of Old Fillings:
Fillings may need to be replaced due to wear and tear or if they are damaged or failing.